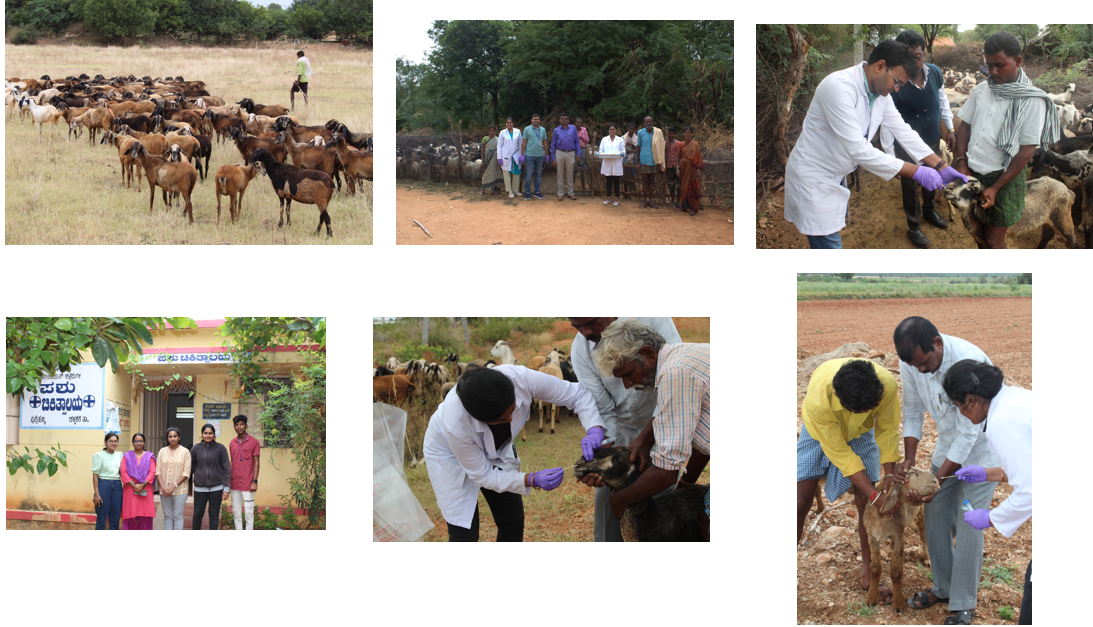
AMU-AMR Livestock Tool
A web-based system for estimating and visualizing antibiotic usage in Dairy Cattle, Small Ruminants, and Poultry.

Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and Antimicrobial Use (AMU)
Surveillance of AMR and AMU is crucial for understanding trends, informing policies, and guiding interventions to combat the global threat of antimicrobial resistance in food animals, the environment, and humans. India has several AMR surveillance programs, but there is an urgent need to integrate them for effective surveillance and mitigation through a One Health approach. Additionally, the association of antibiotic use in animals with the emergence of antibiotic resistance in humans needs further study.
Introduction
Surveillance is the systematic ongoing collection, collation and analysis of data, and the timely dissemination of information to relevant stakeholders, particularly those who are in a position to take action. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance and monitoring -tracks changes and trends in AMR pathogens and resistant determinants. One Health approach will help to integrate findings of antibiotic use (AMU) in animals, humans, plants and the environment. This involves sharing data and information across sectors for a more effective and coordinated response to tackling AMR.
Objectives of AMR surveillance in livestock, humans and environment
- Document prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria over time and geography.
- Understand AMR transmission dynamics across livestock, fisheries, the environment, and humans.
- Forecast the emergence of new drug-resistant bacteria.
- Evaluate epidemiological clones of AMR pathogens.
- Understand the persistence of drug-resistant pathogens.
- Plan, implement, and evaluate treatment strategies.
- Conduct training and awareness programs on AMR stewardship.
Methods of AMR Surveillance
- Laboratory-based: Monitoring resistance in clinical isolates from human and animal health.
- Sentinel Surveillance: Sentinel surveillance: Collecting data from selected healthcare facilities to identify trends.
- Genomic Surveillance:Genomic surveillance of AMR bacteria by using Whole-genome sequencing and metagenomics approach for identifying resistance genes in pathogens.
- Environmental Surveillance: Environmental surveillance: Monitoring resistance in water, soil, and food sources.
Global Initiatives
National AMR Surveillance Programs
- NARS-Net (NCDC): The National AMR surveillance network (NARS-Net) – by NCDC for Humans based on Clinical data
- AMRSN (ICMR): Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN) –by ICMR for Humans based on Clinical data
- AINP-AMR (ICAR): All India Network project on AMR in livestock and fisheries (AINP-AMR) by ICAR for healthy livestock and fisheries sector (No clinical surveillance)
- National One Health Mission: National One Health Mission program- integration of human, animals, plants and environment
- INFAAR (ICAR & FAO): AMR Surveillance Data: In India, ICMR, NCDC and ICAR organisations have separate network projects for AMR surveillance in both humans and livestock sector. For example, National AMR Surveillance network (NARS-Net) was established in 2013 to determine the magnitude and trends of AMR in humans in different geographical regions of the country.
Laboratory techniques employed for AMR surveillance
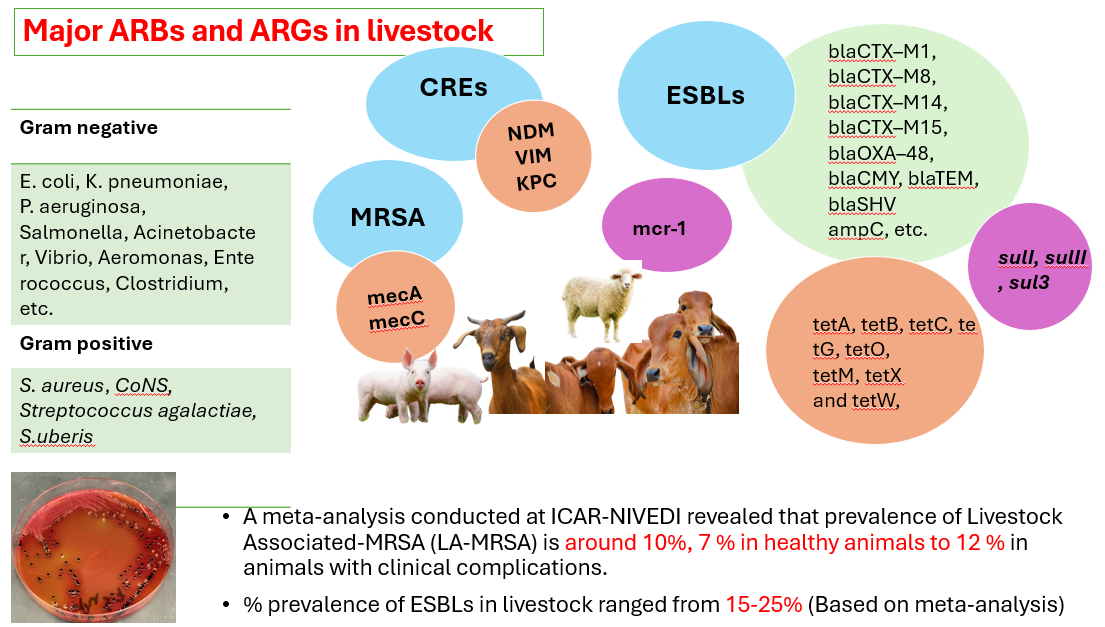
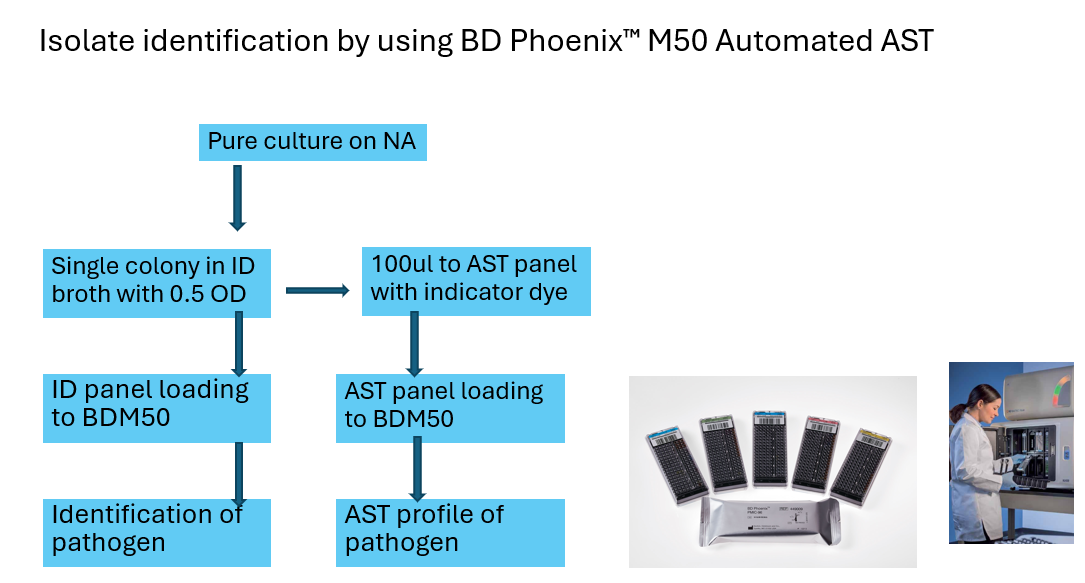
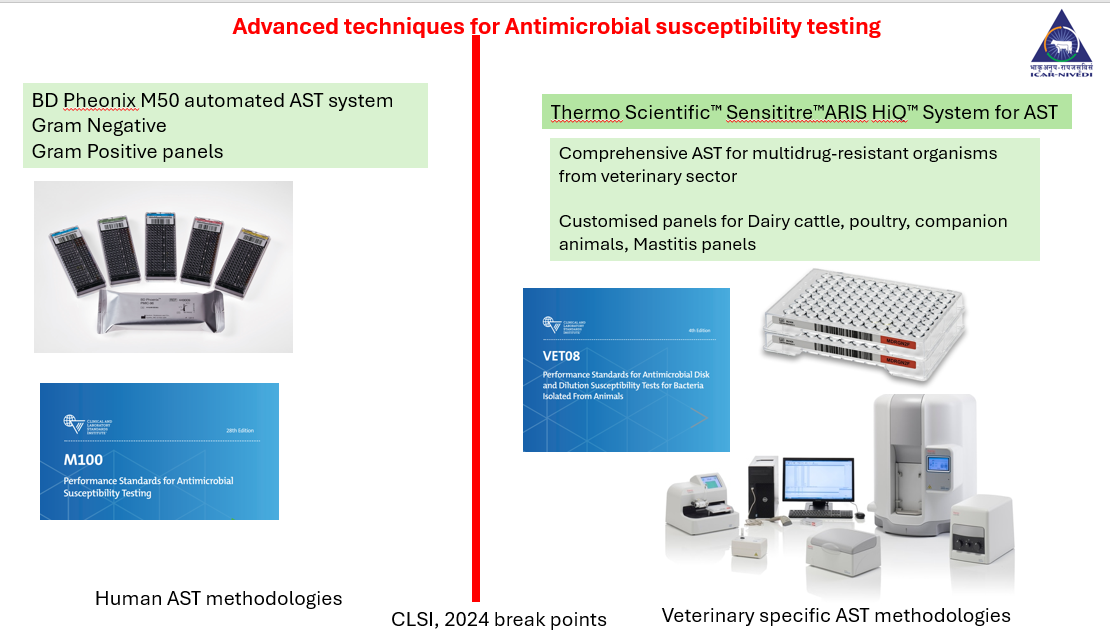
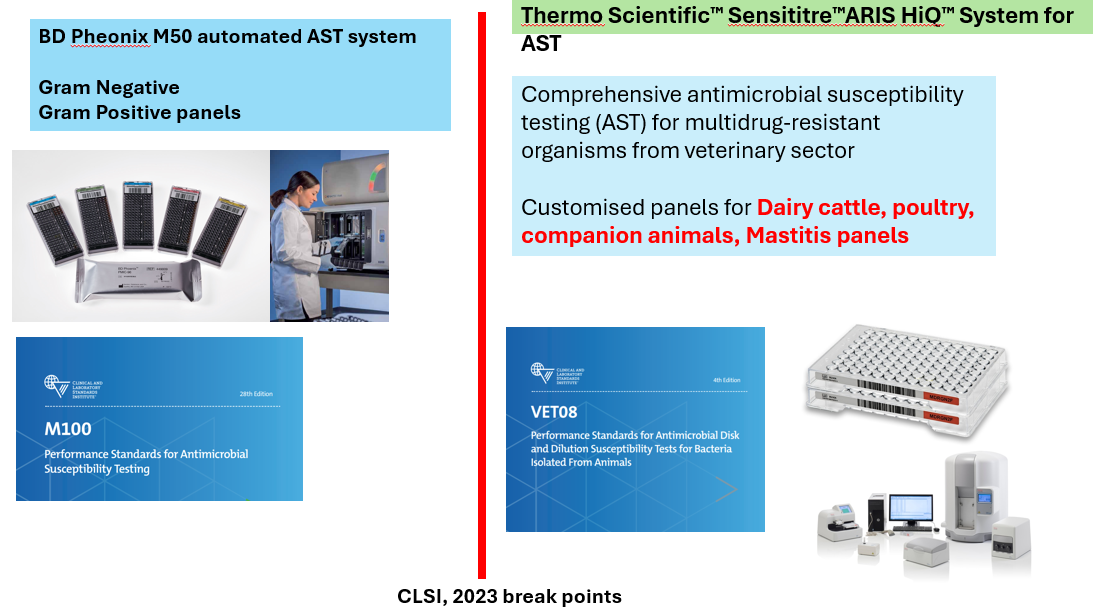
- Phenotypic Methods: Phenotypic Antibiogram methods (AST): Disc diffusion, Automated AST systems (BD-M50, Sensititre and Vitek) as per CLSI 2024 breakpoints of MICs for Grams negative and Grams positive bacteria
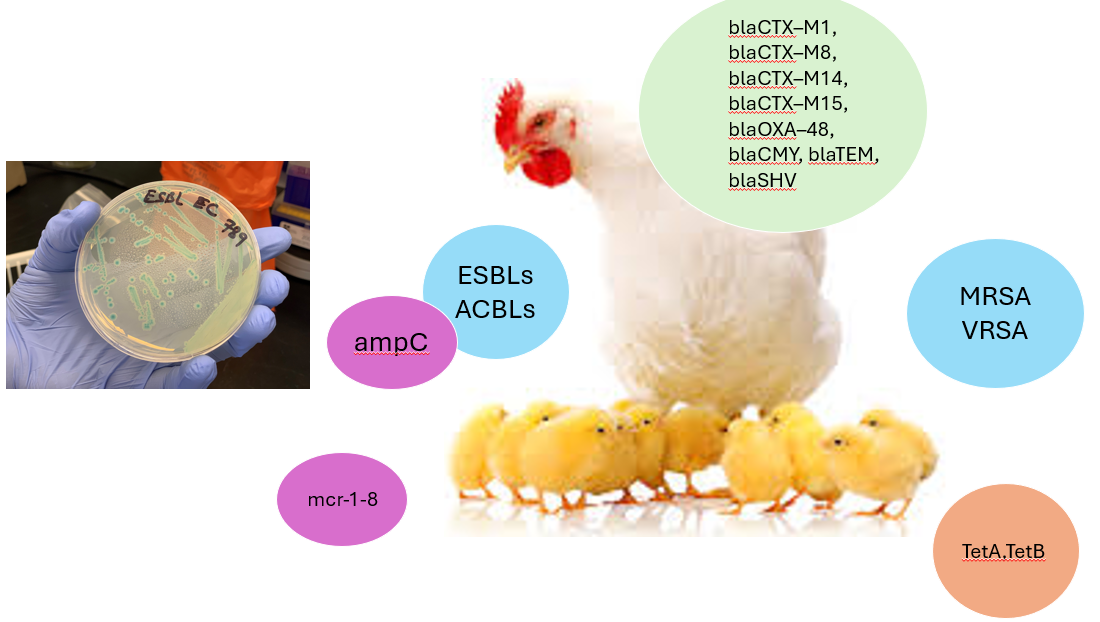
- Genomic Methods: Genomic surveillance methods: Whole genomic sequencing and analysis, metagenomics, amplicon sequencing, etc for ARGs, global clones of staph aureus, ESBLs etc
Methods for AMR surveillance data analysis
Spatial Analysis Techniques:
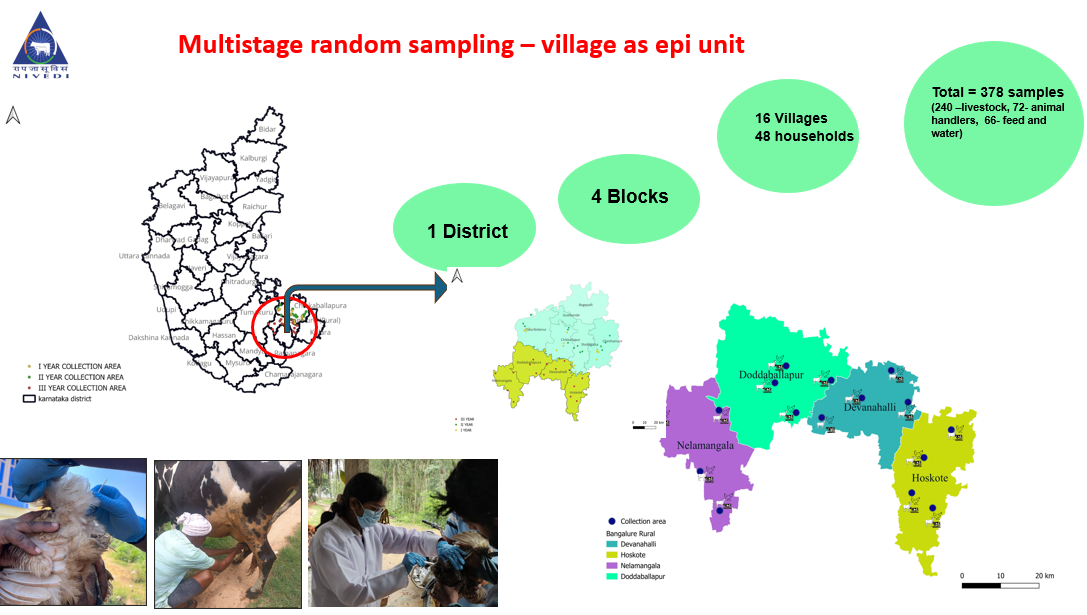
- Mapping:Thematic maps can be created using ArcGIS or Epi info TM to visually represent the spatial distribution of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, clinical cases, antibiotic use pattern, antibiotic resistance pattern, etc to understand the prevalence of AMR in different regions.
- Hotspot Analysis: A hotspot can be defined as an area that has higher concentration of events compared to the expected number. Hotspot analysis is a spatial analysis and mapping technique used for identification of clustering of spatial phenomena.
- Spatial Autocorrelation: It is mainly used to identify whether neighbouring regions exhibit similar outbreak of drug-resistant pathogens or AMR patterns.
- Buffer Analysis: It is used particularly to study the impact of certain features (e.g., urban areas, hospitals, livestock farms) on AMR prevalence.
- Cluster Analysis: The method of identifying similar groups of data in a large dataset is called clustering or cluster analysis.
- Heatmap Analysis:heat map analysis method is being used specifically to map the antibiotic resistance gene repertoire or antibiotic resistance profiles in various settings such as humans, livestock, water and environment.
🌟 Key Features
The AMU Tool systematically tracks antibiotic usage across Dairy Cattle, Small Ruminants, and Poultry.
💊 Total Antibiotic Used (g)
📏 Antibiotics in mg/PCU (mg/kg)
👨🌾 Total Animals Treated (%)
🌿 Total Medicated Rations
📅 Total Treatment Days
📊 Interactive Visualization
Calculation Methods
- % of Treatment Days = (Number of days treated / Total days in production cycle) × 100
- % of Animals Treated = (No. of animals treated / Total animals in the herd) × 100
- % of Medicated Rations = (No. medicated rations / Total rations) × 100
- Total Quantity of Antibiotic Used (g) = (Animals treated × Treatment days × (Average weight of the animals / Selected dose) × Concentration of Antibiotic Ingredient) ÷ 1000
- Antibiotic PCU (mg/kg) = (Total quantity of antibiotic used / Total animals) × Average weight
Reference Resources
- 1. FAO & WOAH. 2023. Guidelines on monitoring antimicrobial use at the farm level – Regional Guidelines for the Monitoring and Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance, Use and Residues in Food and Agriculture
- 2. FAO. 2024. Protocol on estimation of antimicrobial usage at farm level, New Delhi.
- 3. OIE List of Antimicrobials
- 4. ANIMUSE
Get Started Today!
Experience seamless tracking and management of antimicrobial use in livestock farming.
Register here